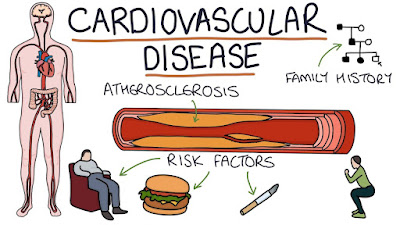
Cardiovascular diseases refer to a group of conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels. Some common cardiovascular diseases include coronary artery disease, heart attack, and stroke. Here's some information about these conditions:
1. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): CAD occurs when the blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle become narrowed or blocked due to the buildup of plaque. This plaque consists of cholesterol, fat, calcium, and other substances. Over time, CAD can cause chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, and may lead to a heart attack.
2. Heart Attack: A heart attack, also known as a myocardial infarction, occurs when there is a sudden blockage of blood flow to a part of the heart muscle. It usually happens when a blood clot forms in one of the narrowed coronary arteries. Symptoms of a heart attack include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, lightheadedness, nausea, and sweating. Prompt medical attention is essential during a heart attack to minimize damage to the heart muscle.
3. Stroke: A stroke occurs when there is a disruption of blood flow to the brain, leading to brain cell damage or death. Ischemic stroke is the most common type and is caused by a blockage in a blood vessel supplying the brain. Hemorrhagic stroke, on the other hand, results from bleeding into the brain. Symptoms of a stroke include sudden weakness or numbness of the face, arm, or leg (usually on one side of the body), difficulty speaking or understanding speech, severe headache, and loss of coordination.
Several risk factors contribute to the development of cardiovascular diseases, including:
1. High blood pressure (hypertension)
2. High cholesterol levels
3. Smoking
4. Diabetes
5. Obesity
6. Lack of physical activity
7. Unhealthy diet (high in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and salt)
8. Family history of cardiovascular diseases
9. Age (risk increases with age)
10. Gender (men are generally at higher risk, although women's risk increases after menopause)
Prevention and management of cardiovascular diseases involve lifestyle modifications and, in some cases, medical interventions. Lifestyle changes may include regular exercise, a healthy diet, weight management, smoking cessation, and stress reduction. Medications such as cholesterol-lowering drugs, blood pressure medications, and blood thinners may be prescribed to manage risk factors and prevent complications.
It's important to note that if you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of a cardiovascular disease, immediate medical attention should be sought.